南湖新闻网讯(通讯员 王利利) 近日,我校生命科学技术学院严顺平教授课题组研究发现了蛋白激酶ATR 和WEE1的下游新组分,完善了ATR信号转导通路,揭示了细胞周期的“刹车”机制。
所有生物都需要把正确的遗传信息(DNA)传递给下一代。但是,DNA 不断地受到各种体外和体内因素的伤害。为了维持基因组的稳定性,所有生物都进化出了复杂而精细的DNA损伤应答机制,包括激活细胞周期检验点、DNA修复、转录调控和细胞凋亡等。细胞周期检验点的激活能使细胞周期进程暂停,以保证细胞有充足的时间进行DNA修复,在DNA损伤应答中发挥关键作用。
蛋白激酶ATR是DNA损伤修复通路中的最核心调控蛋白之一,主要参与DNA复制胁迫应答。在动物中,ATR主要通过调控细胞周期检测点激酶CHK1和细胞周期调控因子CDC25来发挥作用。但是,植物缺少CHK1和CDC25 的同源蛋白,因此ATR在植物中的作用机理尚不清楚。
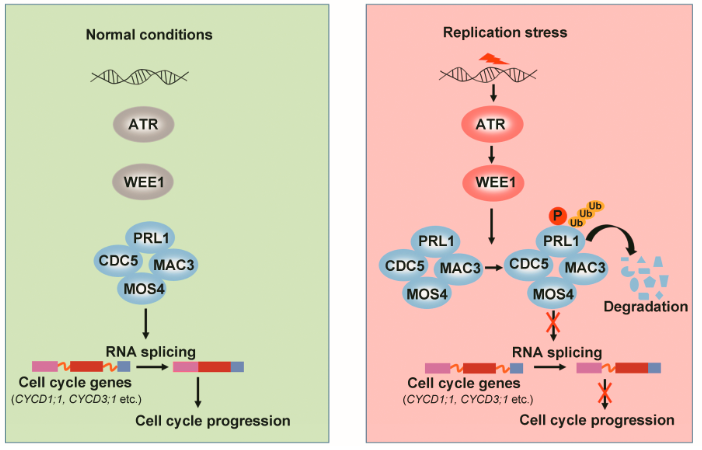
ATR-WEE1激酶模块的工作模型
王利利等人通过遗传筛选atr突变体的抑制子发现,突变MAC复合体(参与前体mRNA的剪接)的核心亚基PRL1能抑制拟南芥atr突变体对DNA复制胁迫诱导剂羟基脲(HU)的超敏感性。通过进一步的遗传学和生物化学研究,他们发现,在DNA复制胁迫发生时,ATR可以激活下游的蛋白激酶WEE1,WEE1通过磷酸化PRL1促进它的降解,PRL1的降解破坏了MAC复合体的功能,导致细胞周期基因的前体mRNA不能被正常剪接,从而阻制细胞周期进程。该研究发现了ATR 和WEE1的下游新组分,完善了植物的ATR信号转导通路,揭示了细胞周期调控的新机制,具有重要的科学意义。
英文摘要:DNA damage response is a fundamental mechanism to maintain genome stability. The ATR-WEE1 kinase module plays a central role in response to replication stress. Although the ATR-WEE1 pathway has been well studied in yeasts and animals, how ATR-WEE1 functions in plants remains unclear. Through a genetic screen for suppressors of the Arabidopsis atr mutant, we found that loss of function of PRL1, a core subunit of the evolutionarily conserved MAC complex involved in alternative splicing, suppresses the hypersensitivity of atr and wee1 to replication stress. Biochemical studies revealed that WEE1 directly interacts with and phosphorylates PRL1 at Serine 145, which promotes PRL1 ubiquitination and subsequent degradation. In line with the genetic and biochemical data, replication stress induces intron retention of cell cycle genes including CYCD1;1 and CYCD3;1, which is abolished in wee1 but restored in wee1 prl1. Remarkably, co-expressing the coding sequences of CYCD1;1 and CYCD3;1 partially restores the root length and HU response in wee1 prl1. These data suggested that the ATR-WEE1 module inhibits the MAC complex to regulate replication stress responses. Our study discovered PRL1 or the MAC complex as a key downstream regulator of the ATR-WEE1 module and revealed a novel cell cycle control mechanism.
论文链接:https://academic.oup.com/nar/advance-article/doi/10.1093/nar/gkaa1082/6101606?searchresult=1
审核:严顺平

