南湖新闻网讯(通讯员 张冰)棉花是重要的纤维与油料作物,干旱胁迫极大程度限制了棉花的生长与区域分布,造成棉花产量和品质的下降。近日,Journal of Advanced Research 在线发表了我校棉花遗传改良创新团队题为“The GhMAP3K62-GhMKK16-GhMPK32 kinase cascade regulates drought tolerance by activating GhEDT1-mediated ABA accumulation in cotton” 的研究论文,该研究揭示了干旱条件下,棉花通过激活MAPK级联GhMAP3K62-GhMKK16-GhMPK32并磷酸化下游靶基因GhEDT1,进而激活ABA合成基因GhNCED3的表达,促进ABA的积累从而参与棉花干旱应答的分子机制,该研究阐明了植物中MAPK级联与ABA信号互作参与植物逆境调控的新机制。
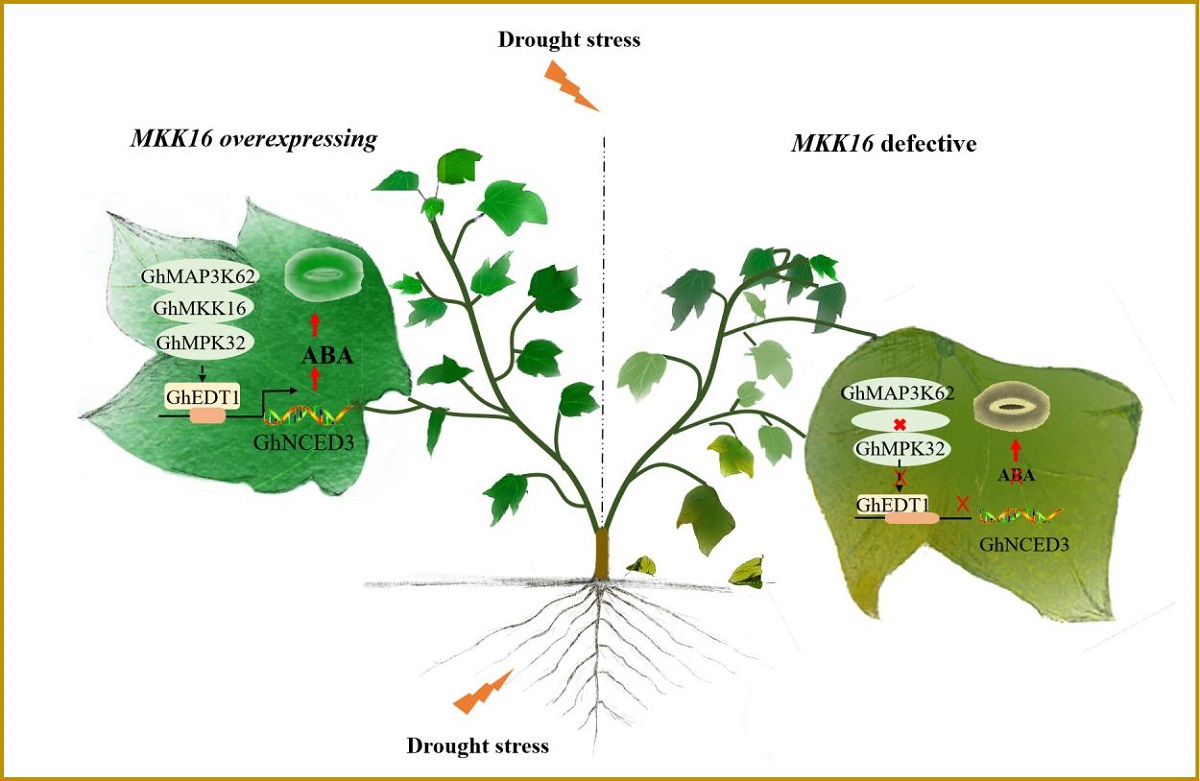
分子模块GhMAP3K62-GhMKK16-GhMPK32-GhEDT1-GhNCED3-ABA调控干旱下棉花可塑性发育
MAPK 级联途径由三个组分组成, 包括 MAPKKK (MAP3K) 、 MAPKK (MKK) 和 MAPK(MPK),是一类重要的信号转导途径,参与调控植物各种生命活动。课题组研究人员对棉花MKK家族成员进行鉴定,发现MAPK 级联关键成员GhMKK16受干旱胁迫显著诱导表达,在棉花对其进行遗传转化,发现其正调控棉花苗期抗旱性,进一步分析表明,棉花叶片的气孔运动与植物激素ABA 的积累在这一过程中发挥了重要作用。
为研究GhMKK16介导的干旱胁迫抗性调控机制,研究人员进一步通过Y2H, BiFC和LCI、磷酸化实验,鉴定到GhMKK16参与MAPK级联通路GhMAP3K62-GhMKK16-GhMPK32,并发现GhMPK32磷酸化激活下游HD-Zip转录因子GhEDT1。VIGS结果显示,在对照中分别沉默GhMA3K62、GhMPK32和GhEDT1的表达,植株在干旱条件下ABA的积累降低,叶片气孔的开度增大,抗旱性降低;而在GhMKK16超表达植株中干涉GhMPK32和GhEDT1的表达,能恢复GhMKK16超表达的相关表型。研究者进一步通过Y1H, EMSA和LUC等技术发现GhEDT1可以结合ABA合成路径关键酶基因GhNCED3启动子区域的HD-box,激活GhNCED3的表达。
综上所述,该研究提出了GhMAP3K62-GhMKK16-GhMPK32级联途径调控靶标GhEDT1进而调控ABA依赖的气孔运动来调控棉花的抗旱性。前期大量研究表明,MAPK级联途径基因的表达受ABA诱导差异表达。该研究发现,GhMAP3K62、GhMKK16 和 GhMPK32 均受 ABA 诱导表达。然而进一步研究显示,通过影响该途径基因的表达可以在干旱胁迫下调节棉花叶片中 ABA 的积累。干旱胁迫下,GhMAP3K62-GhMKK16-GhMPK32 途径在被激活后,会通过下游靶标 GhEDT1 激活 GhNCED3 启动子的活性,促进 ABA 的合成,从而实现对 ABA 信号的反馈调节。因此,该研究首次提出GhMAP3K62-GhMKK16-GhMPK32 途径与 ABA 信号形成闭环形式来参与棉花干旱应答。研究建立的分子调控模块GhMAP3K62-GhMKK16-GhMPK32-GhEDT1-GhNCED3-ABA,丰富了多信号交叉互作协同参与植物干旱应答的分子机制。
华中农业大学作物遗传改良全国重点实验室棉花团队已毕业博士陈林(现就职于武汉生物工程学院)、博士生张冰和硕士生夏林杰为论文共同第一作者,团队杨细燕教授为论文通讯作者,团队学术带头人张献龙教授和英国杜伦大学Keith Lindesy教授参与了该研究的指导工作。该研究得到了国家重点研发计划项目(2018YFD1000907)和中央高校科研业务费(2662020ZKPY011)的资助。
审核人:杨细燕
【英文摘要】
Introduction
Drought is the principal abiotic stress that severely impacts cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) growth and productivity. Upon sensing drought, plants activate stress-related signal transduction pathways, including ABA signal and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade. However, as the key components with fewest members in the MAPK cascade, the function and regulation of GhMKKs need to be elucidated. In addition, the relationship between MAPK module and the ABA core signaling pathway remain incompletely understood.
Objective
Here we aim to elucidate the molecular mechanism of cotton response to drought, with a focus on mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascades activating ABA signaling.
Methods
Biochemical, molecular and genetic analysis were used to study the GhMAP3K62-GhMKK16-GhMPK32-EDT1 pathway genes.
Results
A nucleus- and membrane-localized MAPK cascade pathway GhMAP3K62-GhMKK16-GhMPK32, which targets and phosphorylates the nuclear-localized transcription factor GhEDT1, to activate downstream GhNCED3 to mediate ABA-induced stomatal closure and drought response was characterized in cotton. Overexpression of GhMKK16 promotes ABA accumulation, and enhances drought tolerance via regulating stomatal closure under drought stress. Conversely, RNAi-mediated knockdown of GhMKK16 expression inhibits ABA accumulation, and reduces drought tolerance. Virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS)-mediated knockdown of either GhMAP3K62, GhMPK32 or GhEDT1 expression represses ABA accumulation and reduces drought tolerance through inhibiting stomatal closure. Expression knockdown of GhMPK32 or GhEDT1 in GhMKK16-overexpressing cotton reinstates ABA content and stomatal opening-dependent drought sensitivity to wild type levels. GhEDT1 could bind to the HD boxes in the promoter of GhNCED3 to activate its expression, resulting in ABA accumulation. We propose that the MAPK cascade GhMAP3K62-GhMKK16-GhMPK32 pathway functions on drought response through ABA-dependent stomatal movement in cotton.
论文链接:https://authors.elsevier.com/sd/article/S2090-1232(22)00249-1

