南湖新闻网讯 (通讯员 陈果)近日,国际期刊Nucleic Acids Research在线发表了华中农业大学作物遗传改良全国重点实验室、湖北洪山实验室题为“A novel active transposon creates allelic variation through altered translation rate to influence protein abundance”的研究论文。该研究发现了一个新的活跃转座子,该转座子插入外显子,产生上游开放阅读框(upstream reading frame, uORF),降低蛋白翻译效率和蛋白丰度,进而影响玉米籽粒产量。
转座子也称“跳跃基因”,是一种特殊的DNA序列,可以从基因组一个位置跳跃到另一个位置。20世纪40-50年代,Barbara McClintock女士以玉米为材料,首次在玉米中发现了转座子。她将发现的转座子命名为Ac和Ds,二者构成了Ac-Ds控制体系,其中,Ac是自主型转座子,可以自发跳跃,Ds是非自主型转座子,只有在Ac存在时,才能发生跳跃。起初,转座子理论一直未受重视,但随着其他科学家在细菌等其它多个物种中相继发现了类似现象,McClintock的发现才逐步被人们认可,并最终于1983年获得诺贝尔生理医学奖。
随着研究的深入,人们发现转座子是驱动基因组进化和表型多样性的重要动力。目前,人们发现转座子以多种机制调控基因表达和表型变异,包括插入编码区导致蛋白质结构变异,通过DNA甲基化或者提供新的启动子、增强子等调控元件改变基因表达水平,产生小干扰RNA抑制蛋白翻译等。那么,转座子是否能以其它新机制调控基因表达呢?
本研究中,作者在玉米自交系B73后代材料中发现了一个活跃的转座子,将其命名为BTA(B73 active TE hAT)。BTA插入到编码糖转运蛋白的基因ZmSWEET4c第一个外显子中,形成了一个新的具有剂量效应的亚等位基因,并导致玉米籽粒大小改变。BTA插入不影响基因转录、剪切、亚细胞定位等,但是通过产生uORF及其自身的二级结构抑制了ZmSWEET4c的翻译效率,降低了蛋白质丰度。除此之外,BTA插入其它基因中也会产生相似的效应。通过转座子捕捉技术,在BTA活跃的后代材料中鉴定到79个新的插入事件,其中包括BTA和BTA-like转座子。新的插入位点具有典型的常染色质特征,包括低水平的DNA甲基化和高水平的H3K27ac。研究还鉴定到BTA及BTA-like转座子对应的自主转座酶,它具有完整的ORF,能够转录和翻译,编码的蛋白质具有典型的自主转座酶功能结构域。
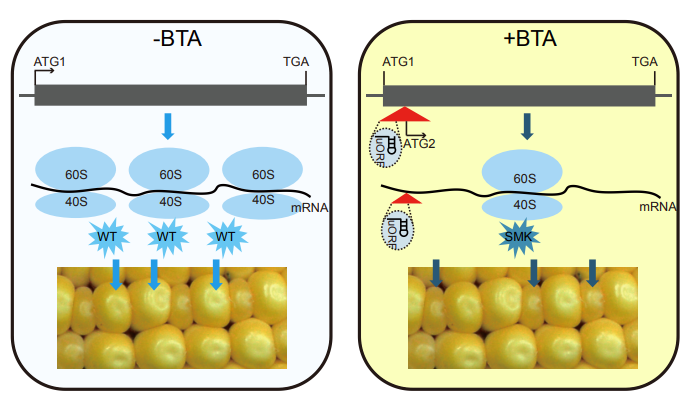
图:转座子调控蛋白质翻译和玉米粒型。
综上,本研究鉴定了玉米和水稻上趋同选择基因ZmSWEET4c的一个有功能且具有剂量效应的亚等位基因。鉴定了一类新的转座子,发现转座子可形成uORF,并通过调控蛋白质翻译效率调控基因表达和表型。本研究为基于转座子驱动的作物改良提供了新的途径,通过对转座子进行编辑,可调控蛋白丰度,创制优良等位基因,实现重要农艺性状的改良。
本文通讯作者是华中农业大学玉米团队李青教授,已毕业博士生陈果(任职于新疆农业科学院核技术生物技术研究所),在读硕士生王锐林,在读博士生江宜哲为共同第一作者。明尼苏达大学Nathan Springer教授参与了相关研究工作。本研究获得国家自然科学基金、中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金和高等学校学科创新引智计划等的资助。
【英文摘要】
Protein translation is tightly and precisely controlled by multiple mechanisms including upstream open reading frames (uORFs), but the origins of uORFs and their role in maize are largely unexplored. In this study, an active transposition event was identified during the propagation of maize inbred line B73. The transposon, which was named BTA for ‘B73 active transposable element hAT’, creates a novel dosage-dependent hypomorphic allele of the hexose transporter gene ZmSWEET4c through insertion within the coding sequence in the first exon, and results in reduced kernel size. The BTA insertion does not affect transcript abundance but reduces protein abundance of ZmSWEET4c, probably through the introduction of a uORF. Furthermore, the introduction of BTA sequence in the exon of other genes can regulate translation efficiency without affecting their mRNA levels. A transposon capture assay revealed 79 novel insertions for BTA and BTA-like elements. These insertion sites have typical euchromatin features, including low levels of DNA methylation and high levels of H3K27ac. A putative autonomous element that mobilizes BTA and BTA-like elements was identified. Together, our results suggest a transposon-based origin of uORFs and document a new role for transposable elements to influence protein abundance and phenotypic diversity by affecting the translation rate.
论文链接:https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac1195
审核:李青