南湖新闻网讯(通讯员 李书挺)近日,我校理学院韩鹤友教授团队通过仿生纳米递送天然水蛭素,实现了无创溶栓和有效抗凝。相关成果以“Biomimetic Nanoplatelets to Target Delivery Hirudin for Site-Specific Photothermal/Photodynamic Thrombolysis and Preventing Venous Thrombus Formation”和“Platelet-Covered Nanocarriers for Targeted Delivery of Hirudin to Eliminate Thrombotic Complication in Tumor Therapy”为题,在线发表在Small和ACS Nano杂志上。本研究创建了一种基于血小板膜的仿生纳米递送平台,将水蛭素靶向递送至血栓部位,实现了无创溶栓和有效抗凝。
血栓对人体健康造成的危害很大,包括对脑、心脏、肺部、肾脏及下肢血管等造成的危害。临床上治疗血栓主要是手术干预和溶栓,其中手术的缺点是侵入性、不方便、治疗费用和治疗风险等;而注射药物溶栓或抗血栓成为优选的治疗方法,但其受药物半衰期短的限制,多数抗血栓药物被迫在短期内以高剂量重复给药以获得有效的溶栓作用,结果导致出血及并发症等。因此,有效、安全、非药物溶栓的纳米治疗倍受关注。
水蛭(又称蚂蟥),主要生长在湖泊、河流等湿地环境,是经典的活血化瘀中药,《神农本草经》中记载水蛭有活血、散淤和通经的功效。水蛭素是从水蛭唾液腺提取的主要活性物质,由65或66个氨基酸残基组成的单链多肽。水蛭素是天然的凝血酶特异性抑制剂,具有很强的抗凝血活性,并且耐高温。水蛭素是直接抗凝血酶的药物,与肝素不同,水蛭素直接与凝血酶结合形成不可逆的复合物,其抗凝作用不仅具有特异性,而且抗凝效果显著。
纳米递送平台治疗血栓需要解决以下三大问题:一是纳米药物在血栓部位的高浓度富集。二是溶栓药物可引起不良组织或部位出血,甚至引起其他心血管疾病或器官损害。利用血栓部位的特殊微环境,提供仿生纳米给药系统,实现药物只能在血栓部位靶向释放,克服生物屏障并提高药物的治疗指数。三是实时成像不仅可以将血栓斑块与其他正常组织区分开来,还可以提供血栓的详细信息。因此,影像引导下的治疗是个性化治疗的关键因素。
血小板膜(PM)具有聚集血栓斑块的能力,可将其用于仿生纳米给药治疗血栓。如图1所示,韩鹤友教授团队采用短期溶栓与长期抗凝相结合的策略,搭建了一种具有血小板膜修饰的卟啉共价有机框架纳米平台,黑色素(源自墨鱼)共价接枝卟啉COF,将水蛭素加载到的孔中,并进一步涂覆血小板膜,以获得 HMPC@PM(图 1a)。水蛭素可靶向递送至血栓部位,在激光照射下,通过热疗和活性氧进行无创伤溶栓治疗。这种双模式溶栓有效地避免了来自破碎纤维蛋白的微小碎片的再栓塞。更为重要的是缓慢释放的水蛭素的可有效防止血栓复发(图1b)。
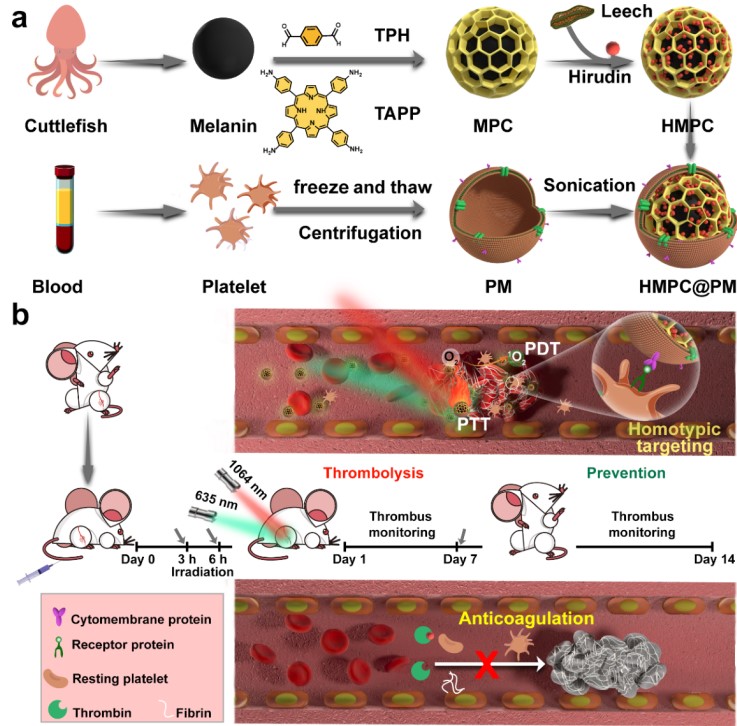
图1. HNPC@PM 仿生纳米递送平台制备及其水蛭素溶栓机制
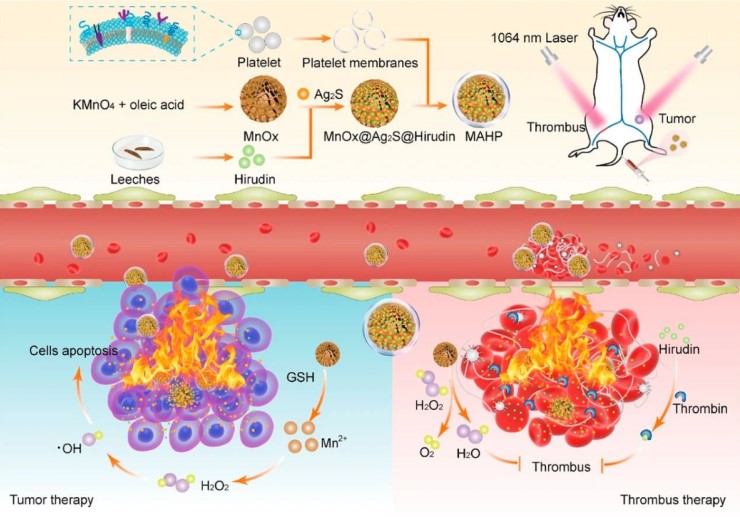
图2. MAHP仿生纳米递送平台制备及其同时治疗肿瘤和肿血栓
ACS Nano杂志发表文章的题目为Platelet-Covered Nanocarriers for Targeted Delivery of Hirudin to Eliminate Thrombotic Complication in Tumor Therapy”,如图2所示,论文研究开发了一种血小板膜修饰的仿生MnOx/Ag₂S纳米花平台(MAHP),结果显示,血小板膜的修饰后可显著延长药物血液循环时间,MAHP具有良好的血栓和肿瘤的靶向能力,实现了肿瘤治疗和血栓治疗的双重功能。
综上,本研究工作为治疗血栓相关疾病提供了新的思路。
我校博士研究生李书挺、张凯和马召玉为该论文共同第一作者(Small),韩鹤友教授为论文的通讯作者。该项工作得到了国家自然科学基金的资助。
英文摘要(Small):Due to the high recurrence rate and mortality of venous thrombosis, there is an urgent need for research on antithrombotic strategies. Because of the short half-life, poor targeting capabilities, bleeding complications, and neurotoxic effects of conventional pharmacological thrombolysis methods, it is essential to develop an alternative strategy to non-invasive thrombolysis and decrease the recurrence rate of venous thrombosis. We first propose a platelet-mimetic porphyrin-based covalent organic framework-engineered melanin nanoplatforms to target delivery of hirudin to the vein thrombus site for noninvasive thrombolysis and effective anticoagulation. Owing to the thrombus-hosting properties of platelet membranes, the nanoplateform could target the thrombus site and then activate hyperthermia and reactive oxygen species for thrombolysis under near-infrared light irradiation. The PTT/PDT combo could substantially improve the effectiveness (85.7%) of thrombolysis and prevent secondary embolism of larger fragments. Afterward, the highly loaded (97%) and slow-release hirudin (14 days) were effective in preventing the recurrence of blood clots without the danger of thrombocytopenia. The described biomimetic nanostructures offer a promising option for improving the efficacy of thrombolytic therapy and reducing the risk of bleeding complications in thrombus associated diseases.
文章链接:https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202203184
https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.2c06666
审核人:韩鹤友

