南湖新闻网讯(通讯员靳婕仔)近日,我校资源与环境学院国家环境保护土壤健康诊断与绿色修复重点实验室土壤化学与环境团队在铁(氢)氧化物的可变反应活性预测方面取得新进展,相关研究成果以“GenericCD-MUSIC-eSGC model parameters to predict the surface reactivity of iron(hydr)oxides”为题发表在了Water Research上。
铁(氢)氧化物是土壤和沉积物中重要的活性组分之一,具有比表面积大、吸附能力强等特点,其界面反应活性对元素的形态转化和生物有效性起着关键作用。基于铁(氢)氧化物表面反应活性和界面过程构建的机理量化模型不仅能更快捷、高效地揭示元素的原位形态特征,还能预测响应环境条件动态变化的形态转化。然而,天然铁(氢)氧化物种类繁多,形貌多变,其反应活性的多样性导致了模型参数的冗余,现有模型仅适用于详细表征的合成铁(氢)氧化物,对于土壤和沉积物中未知形貌和电荷行为的天然铁(氢)氧化物,缺乏一套“通用”参数来准确预测其可变反应活性,对评估其对元素地球化学行为的影响造成了一定的阻碍。
基于现有模型在实际环境中推广应用难的问题,土壤化学与环境课题组从铁(氢)氧化物的基本结构和形貌出发,通过铁(氢)氧化物表面电荷数据库构建和二次挖掘,确定了铁(氢)氧化物模型参数与形貌的内在关联,推导了电荷分配-多位点表面络合(CD-MUSIC)模型的通用质子吸附参数。该参数不仅反映了不同铁(氢)氧化物结构与反应活性的内在联系,也体现了不同铁(氢)氧化物的同源性和异质性。通用CD-MUSIC-eSGC模型参数的主要优点在于:(1)无需复杂的性质表征,即可准确描述铁(氢)氧化物的反应活性;(2)简化了模型的计算过程和强度。本研究是推动化学形态模型应用于实际土壤环境的关键一步,可为土壤元素循环过程调控和有效性评估等提供理论支撑。
我校资源与环境学院博士研究生靳婕仔为论文第一作者,熊娟副教授为通讯作者,资源与环境学院谭文峰教授、汪明霞教授、侯静涛副研究员,Wageningen大学LuukKoopal教授、中国热带农业科学院梁雨副研究员等参与了研究工作。该研究得到了国家自然科学基金和中央高校基本科研业务专项资金项目资助。
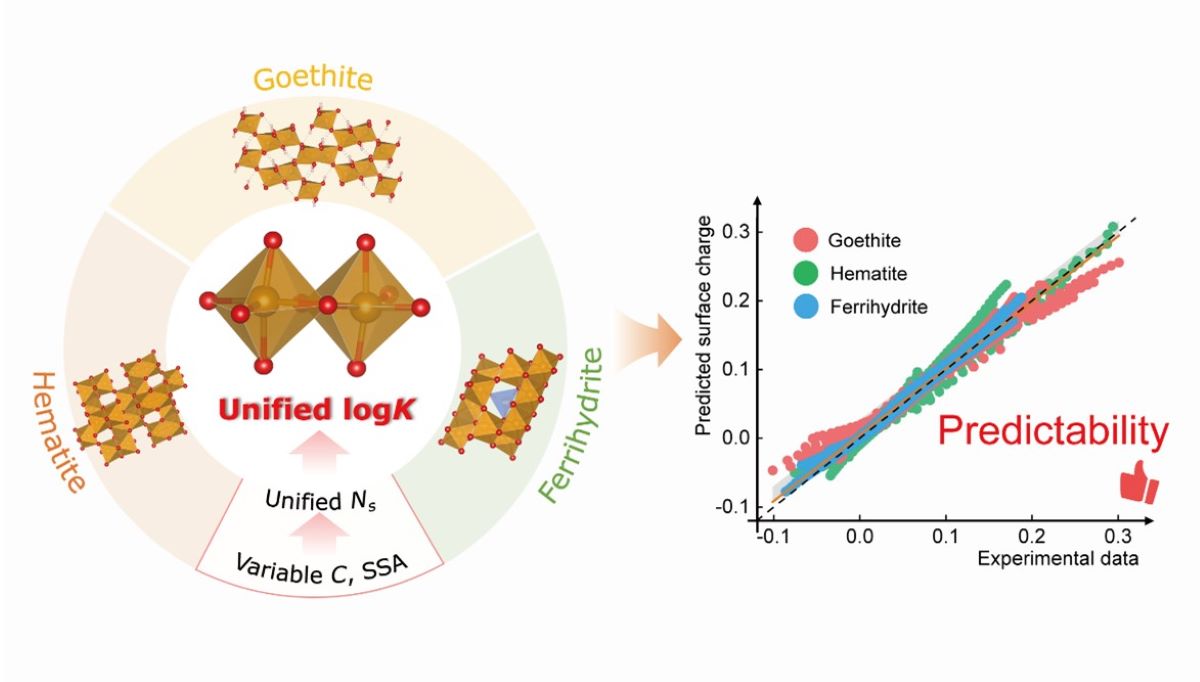
通用CD-MUSIC-eSGC模型参数对铁(氢)氧化物表面反应活性的预测性能
【英文摘要】
The surface reactivity of iron (hydr)oxides plays a crucial role in controlling their interfacial reactions, for which various surface complexation models have been developed. The diversity of mineralogical properties of iron (hydr)oxides has resulted in a redundancy of model parameters, which hampers the modeling of iron (hydr)oxides in soils and sediments, where goethite, hematite and ferrihydrite dominate the iron (hydr)oxide mass fraction. To capture their combined surface reactivity, optimized generic protonation parameters of the Charge Distribution-Multisite Complexation (CD-MUSIC) extended-Stern-Gouy-Chapman (eSGC) model were derived by reanalyzing literature datasets and tested with some newly synthesized iron (hydr)oxides. It was observed that the proton and monovalent ion affinity constants of the different iron (hydr)oxides were located in a narrow range. For the singly- and triply-coordinated hydroxyl sites the obtained generic log(affinity constants) were 8.3 and 11.7 for the protonation reaction and -0.5 for the reaction with the monovalent background ions. Their combination with fixed site densities of singly-/triply-coordinated hydroxyl sites of 3.45/2.70, 5.00/2.50, and 5.80/1.40 sites/nm2for goethite, hematite, and ferrihydrite, respectively, provided good results. The Stern layer capacitances of the inner and outer Stern layers were set equal and could be acquired by an empirical correlation with the sample specific surface area (SSA). The CD-MUSIC-eSGC model with the generic model parameters enables good quality predictions of the proton reactivity of iron (hydr)oxides in 1:1 electrolyte solutions regardless of the sample heterogeneity. The advantages of the generic CD-MUSIC-eSGC model are twofold: (1) protonation of iron (hydr)oxides can be described without making use of spectroscopic measurements and proton titrations, and (2) the model calculations are greatly simplified.
论文链接:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0043135422014798?via%3Dihub
