南湖新闻网讯(通讯员 段子豪)近日,我校资源与环境学院国家环境保护土壤健康诊断与绿色修复重点实验室土壤化学与环境团队,在不同种植体系镉(Cd)污染生物炭修复效果评估方面取得新进展,相关成果发表在Journal of Hazardous Material上。
Cd是我国农田土壤的首要污染物,具有较高的毒性与迁移性,易在水稻、小麦、玉米等主粮的食用部分富集,对人类健康安全构成重大威胁。生物炭因其原位、绿色、可持续性等特征,在降低Cd污染方面极具潜力,被广泛应用于Cd污染土壤的修复治理。然而,生物炭理化性质多变,且应用场景复杂,现有研究对生物炭修复效果的差异性缺乏统一认识。
鉴于此,我校土壤化学与环境团队通过meta分析,量化生物炭在淹水禾谷类、旱地禾谷类、非禾谷类种植体系中对Cd污染土壤修复效果,结合单因素荟萃回归(Single Meta-regressions)和随机森林机器学习(Random Forest),明确了生物炭修复的关键影响因素。研究结果表明,生物炭能显著降低各种植体系土壤、植物根系和可食用部分的Cd含量,下降幅度在24.9%-45.0%之间。生物炭的原料、施用量、pH以及土壤pH和阳离子交换量是影响生物炭Cd修复效果的关键因素。木质纤维素和草本生制备的物炭适用于所有种植体系,而粪便、木材和生物质为前驱物的生物炭在谷类种植体系中的效果有限。通过控制生物炭制备条件并匹配适用场景,可极大提升修复效果并降低环境经济成本,该结论可为实现污染土壤精准高效修复,农业绿色可持续发展提供理论依据和科技支撑。
此外,本研究还发现生物炭对水稻土的修复效果比旱地更持久,这可为降低生物炭老化不利影响,近一步优化土壤重金属修复策略提供新思路。
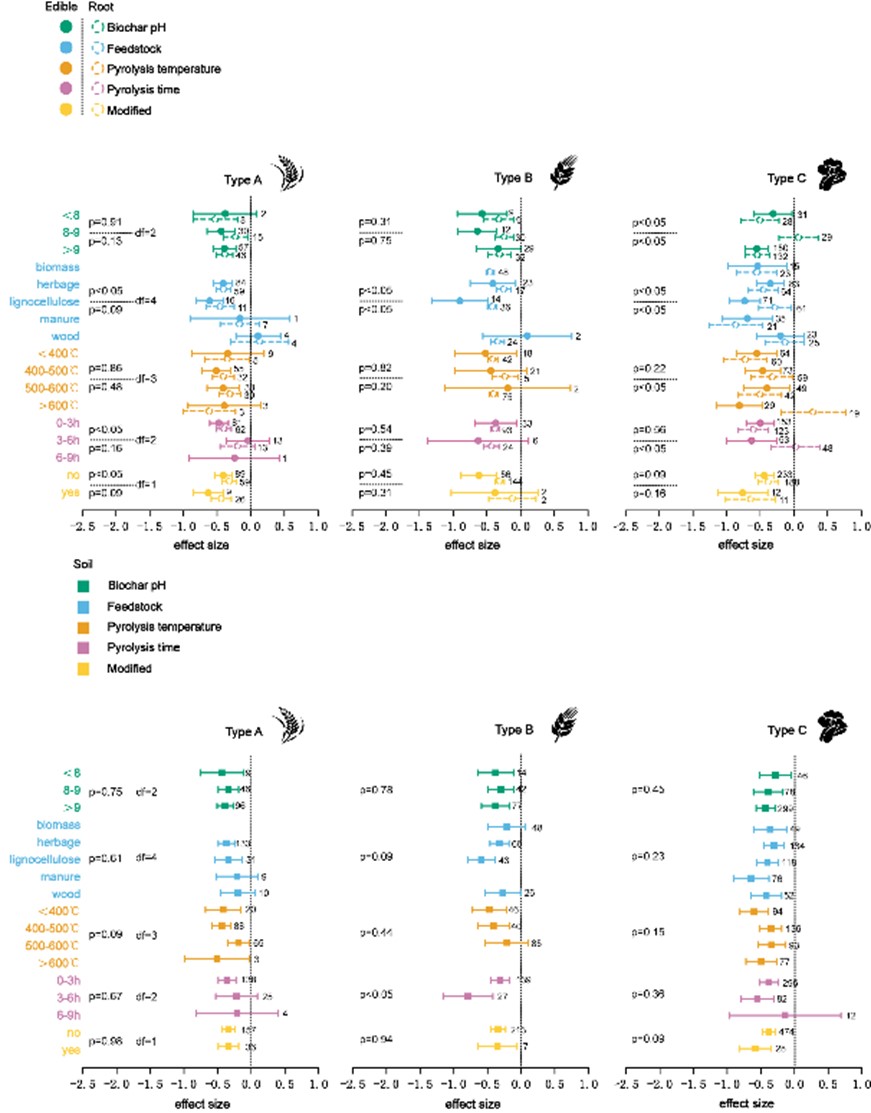
图1.不同生物炭制备参数和理化性质对镉生物有效性和生物累积的影响
我校资环学院硕士研究生段子豪为论文第一作者,博士后陈畅为论文通讯作者,资环学院谭文峰教授、王真教授、熊娟副教授、倪春兰博士以及湖北省生态环境科学研究院蔡俊雄教授为共同作者。该研究得到了国家自然科学基金和湖北省自然科学基金的支持。
【英文摘要】
Cadmium (Cd) poses great threats to human health as a major contaminant in agricultural soil. Biochar shows great potential in the remediation of agricultural soil. However, it remains unclear whether the remediation effect of biochar on Cd pollution is affected by various cropping systems. Here, this study used 2007 paired observations from 227 peer-reviewed articles and employed hierarchical meta-analysis to investigate the response of three types of cropping systems to the remediation of Cd pollution by using biochar. As a result, biochar application significantly reduced the Cd content in soil, plant roots and edible parts of various cropping systems. The decrease in Cd level ranged from 24.9% to 45.0%. The feedstock, application rate, and pH of biochar as well as soil pH and cation exchange capacity were dominant factors for Cd remediation effect of biochar, and their relative importance all exceeded 37.4%. Lignocellulosic and herbal biochar were found to be suitable for all cropping systems, while the effects of manure, wood and biomass biochar were limited in cereal cropping systems. Furthermore, biochar exhibited a more long-lasting remediation effect on paddy soils than on dryland. This study provides new insights into the sustainable agricultural management of typical cropping systems.
论文链接:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.130939
审核人:谭文峰
