南湖新闻网讯(通讯员 李楚仪)近日,我校工学院牛文娟副教授课题组和农业农村部规划设计研究院孟海波研究员的研究成果以“Microwave–assisted hydrothermal conversion of crop straw: Enhancing the properties of liquid product and hydrochar by varying temperature and medium”为题在Energy Conversion and Management发表。该研究报道了秸秆在不同温度和不同水热介质条件下进行微波水热反应,探索了秸秆微波水热反应过程机理,并且优化了最佳反应条件。
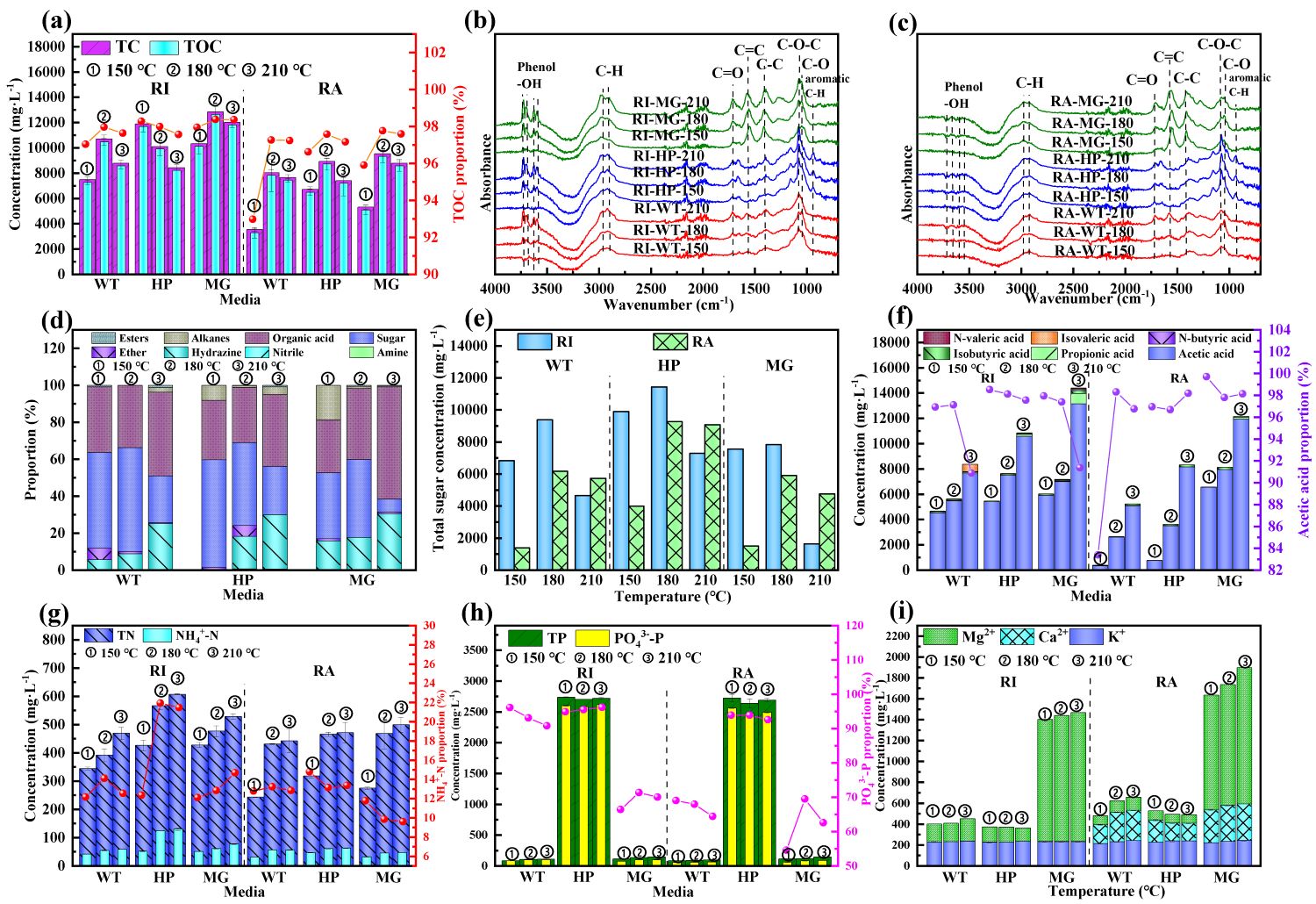
秸秆微波水热液体的组成成分
秸秆是天然的有机物,以木质纤维素为主,包括纤维素(40–50%)、半纤维素(15–35%)和木质素(20–30%)。木质纤维素是自然界丰富存在的天然有机物,可以通过生物精炼创造多种产品,包括生物衍生聚合物等,具有多种潜在应用价值。微波水热技术可以实现秸秆的多组分转化与利用,极大地回收了秸秆中的碳元素,减少了碳元素向大气中的迁移,有利于促进我国“碳中和”目标的实现,环境效益显著。同时,秸秆水热固液产物具有较高的附加值,微波水热技术有利于实现秸秆的高效转化与高值化利用。
该研究探究了不同水热温度和不同介质下,秸秆微波水热液体和水热炭的形成机制和产物理化特性。提高水热温度以及添加磷酸和乙酸镁,均提高了水热液体的有机物和营养离子的浓度。乙酸镁促进了秸秆水热反应中的糖类向酸类的转化,使水热液体产物中的总有机化合物、总有机酸的浓度和电导率最高。
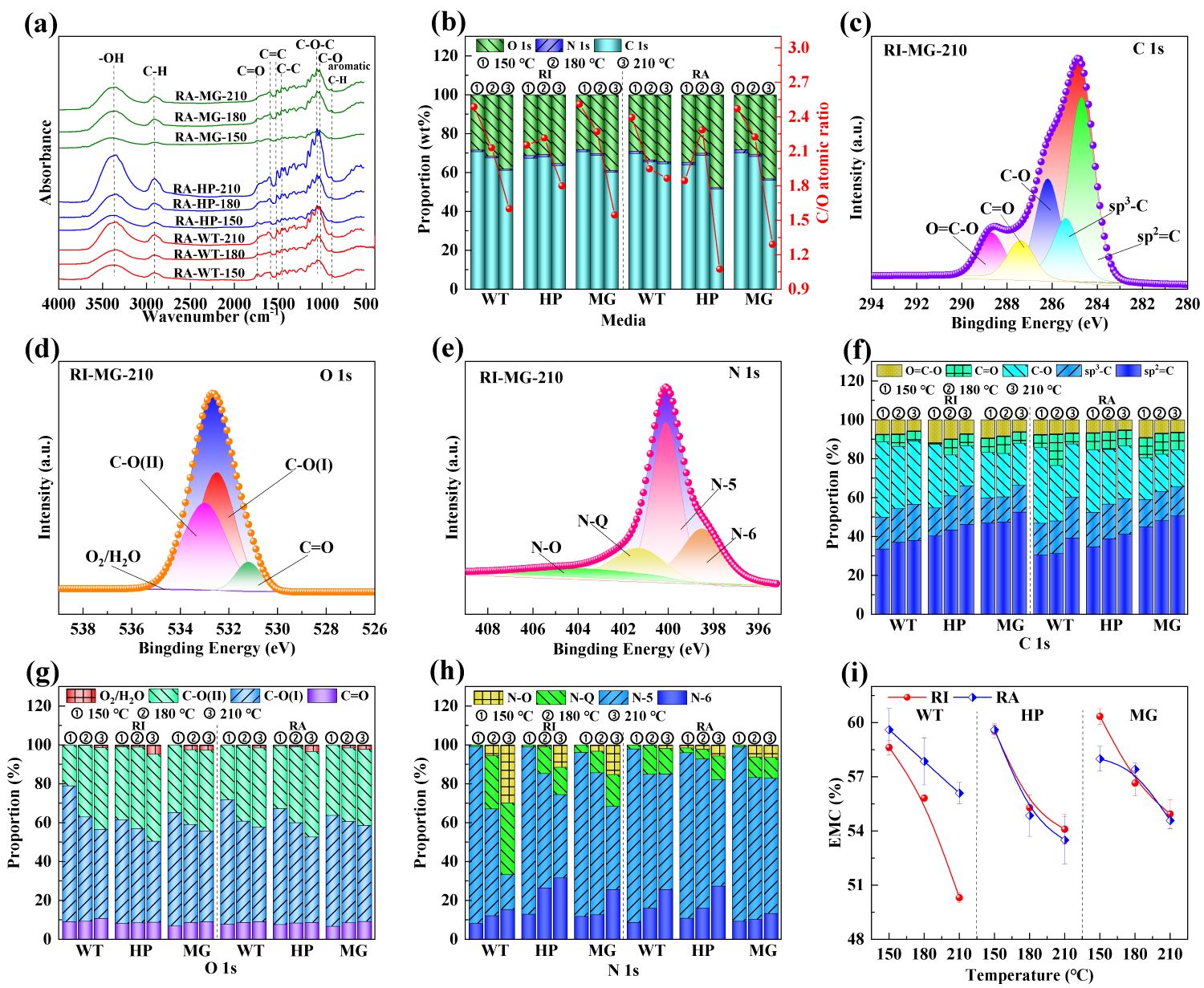
秸秆微波水热炭活性位点与润湿性分析
随着水热温度的升高,水热炭的结晶度和孔隙结构增加,但水热炭产率和表面活性基团减少,如C-O和N-5。乙酸镁介质有利于水热炭有序碳结构的生成,并能增加水热炭表面含氮和含氧基团,同时降低水热炭的结晶度。水热炭的润湿性仍然保持在较高的水平,这表明它有作为高品质多孔炭前驱体和碳基吸附材料的潜力。在乙酸镁介质中,当水热温度为180 °C时,液体产物中积累的有机物最多,有机碳浓度为12662 mg/L,水热炭拥有更多活性基团。通过水热炭产率和液体有机碳浓度的相关文献比较表明,乙酸镁介质对提高水热炭产率和水热液体总有机碳浓度的作用显著。水热温度和介质的工艺优化有利于提高秸秆微波水热产物性能,为秸秆的微波水热转化技术和固液产物的增值利用提供理论基础和技术支持,有利于实现秸秆的高效转化与高值化利用。
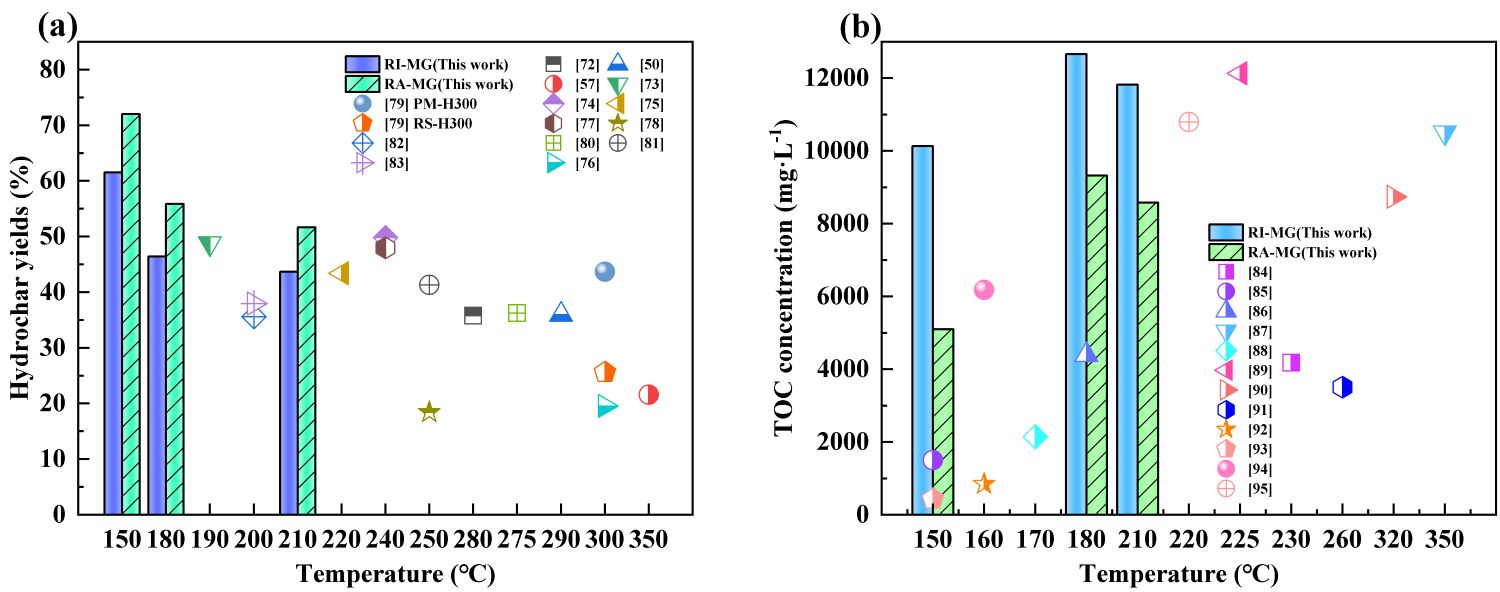
水热炭产率和液体有机碳浓度的相关文献比较
华中农业大学工学院2020级硕士研究生李楚仪为论文的第一作者,工学院牛文娟副教授和农业农村部规划设计研究院孟海波研究员为论文共同通讯作者,袁巧霞教授和钟菲副教授等为参与作者,华中农业大学为第一完成单位。该研究得到了湖北省自然科学基金面上项目和农业农村部重点实验室的支持。
审核人 袁巧霞
【英文摘要】
Crop straw is gaining increasing attention as a green resource to be converted into biofuels, chemicals, and biomaterials through microwave-assisted hydrothermal conversion (MHTC). To reduce the energy consumption and improve the product quality, this research investigated the properties and formation mechanisms of products obtained from crop straws through MHTC by varying media and temperature. Increasing temperature, phosphoric acid, and magnesium acetate could promote the liquid yield, and increase the concentrations of organic matter and nutrient ions such as K+, Ca2+,and Mg2+of liquid product. Magnesium acetate, whose liquid product exhibited the highest concentration of total organic carbon, further facilitated the conversion of sugars to acids, resulting in acidic liquid products with high electrical conductivity. Increasing temperature improved the crystallinity and pore structure of hydrochar, but reduced the hydrochar yield and surface active groups. Magnesium acetate was beneficial to generate ordered carbon structure, surface nitrogen- and oxygen-containing groups, and reduced the crystallinity of the hydrochar. The pH of liquid product in the phosphoric acid medium was the lowest, which improved the pore volume, the particle size of carbon microspheres, and the amount of carbon microspheres of hydrochar. Hydrochar exhibited good wettability and could be used as a precursor for high quality activated carbon. Compared with previous research, under the temperature of 180 °C in the magnesium acetate medium, nutrients were more preferentially accumulated in the liquid products and the hydrochar possessed more active groups. This work provides a theoretical reference and technical support for MHTC of crop straws and value-added utilization of the solid-liquid products.
论文链接:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0196890423005381
