南湖新闻讯(通讯员 伍贝贝)近日,我校资源与环境学院污水处理与资源化团队在菌藻生物膜反应器中氮代谢机制方面的最新研究成果以“Biofilm bioactivity affects nitrogen metabolism in a push-flow microalgae-bacteria biofilm reactor during aeration-free greywater treatment”为题在Water Research上发表。
微藻-细菌共生聚集体由于其在废水处理过程中的低能量投入和高资源回收潜力而受到广泛关注。然而,快速形成高效、稳定、多功能生物膜是藻菌共生系统在污水处理高效低能耗工程化应用的重要前提。藻菌生物膜的形成和表征对于揭示氮转化和迁移的内在机制具有重要意义。尽管藻菌生物膜在污水高效脱氮的应用日益增多,但生物膜生物活性对污染物去除和氮代谢影响的研究仍然有限。
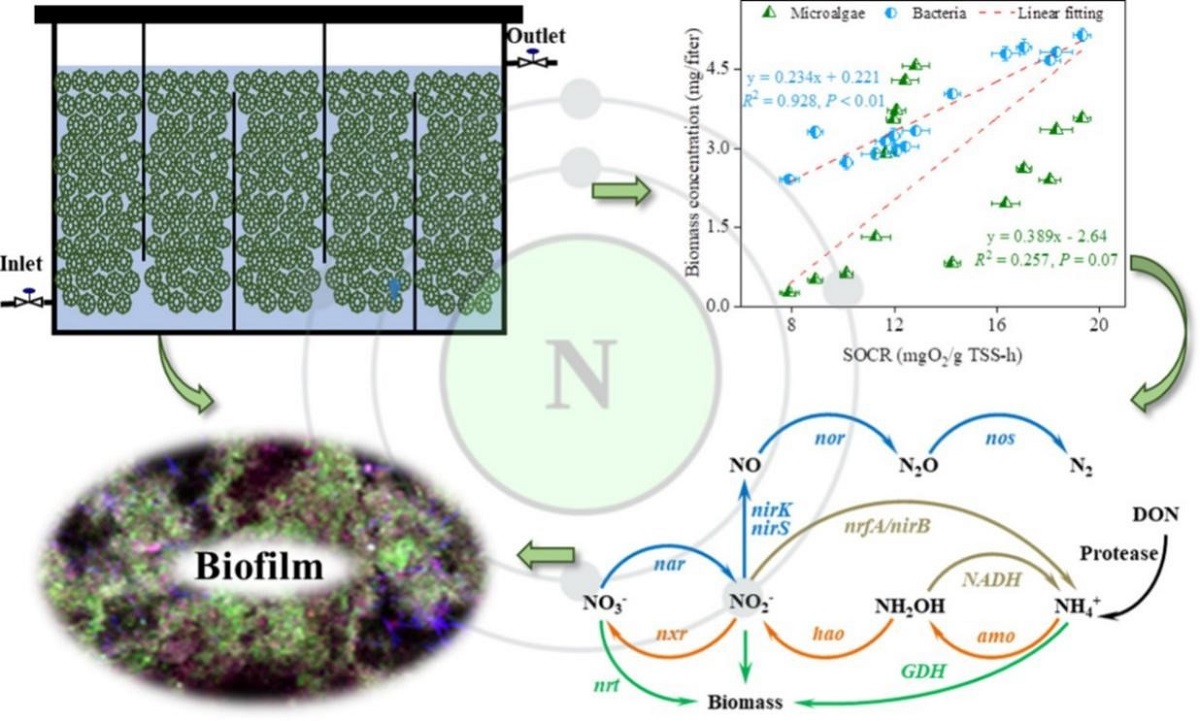
推流式菌藻共生系统中生物膜活性与藻、菌浓度的相关性及氮代谢模式图
基于此背景,团队开发了一种推流式藻菌生物膜反应器用于无曝气灰水处理。系统研究了不同反应器区域生物膜特性、比耗氧量和生成速率以及反应器性能和出水溶解有机氮响应有机负荷的变化,跟踪了对氮代谢起作用的酶的动力学。结果表明,自产氧的藻菌生物膜可实现高效低能耗的灰水处理,系统中高浓度微藻导致高氧气产量,利于污染物的高效去除和出水中溶解性有机氮的减排,而低残留量表明活性剂导致较低氧气消耗速率和微藻的进一步富集,系统中的氮主要以同化作用固定在新和成的生物质中。本工作的结果有望通过优化基于生物膜生物活性的运行条件,实现藻菌生物膜高效低能耗污水处理的工程化应用。
本研究从生物膜活性和氮代谢角度对藻菌生物膜高效氮固定的增效途径提供了新见解,突显了藻菌生物膜在低成本污水处理中的巨大潜力,强调在应对温室气体减排时,应加强藻菌生物膜的N2O减排潜力、途径和控制策略方面的深入研究。
研究得到国家自然科学基金项目和华中农业大学高层次人才项目资助。我校资源与环境学院博士研究生伍贝贝为论文第一作者,周云教授为论文通讯作者。博士研究生崔晓彩,硕士研究生冉婷、李倩和本科生刘思贝也参与了研究工作。
【英文摘要】
Non-aeration microalgae-bacteria biofilm has attracted increasing interest for itsapplication in low cost wastewater treatment. However, it is unclear the quantified biofilm characteristics dynamics and how biofilm bioactivity affects performance and nitrogen metabolisms during wastewater treatment. In this work,a push-flow microalgae-bacteria biofilm reactor (PF-MBBfR) was developed for aeration-free greywater treatment. Comparatively, organic loading at 1.27 ±0.10 kg COD/(m3d) gave the highest biofilm concentration, density,specific oxygen generation (SOGR) and consumption rates (SOCR), and pollutants removal rates. Contributed to low residual linear alkylbenzene sulfonates and bioactivity, reactor downstream showed low bacteria and protein concentrations and SOCR (12.8 mg O2/g TSS h), but high microalgae, carbohydrate,biofilm density, SOGR (49.4 mg O2/g TSS h) and pollutants removal rates. Dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) showed higher molecular weight, CHONS and fraction with 4 atoms of N in reactor upstream. Most of nitrogen was fixedto newly synthesized biomass during assimilation process by related functionalenzymes, minor contributed to denitrification due to low N2emission. High nitrogen assimilation by microalgae showed high SOGR, whichfavored efficient multiple pollutants removal and reduced DON emission. Our findings favor the practical application of PF-MBBfR based on biofilm bioactivity, enhancing efficiency and reducing DON emission for low-energy-input wastewater treatment.
论文链接:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2023.120461
审核人:周云
