南湖新闻网讯(通讯员 刘国阳)近日,我校工学院夏俊芳教授课题组研究成果以“Measurement and evaluation method offarmland microtopography feature information based on 3D LiDAR and inertialmeasurement unit”为题在土壤科学和耕作研究领域期刊Soil& tillage research发表。该研究提出了基于三维激光雷达与惯性测量单元信息融合的耕作地表形貌特征信息检测与评估方法,为评价农田耕作质量提供了一种高效的技术手段,同时降低了农田地表土壤粗糙度的测量误差。
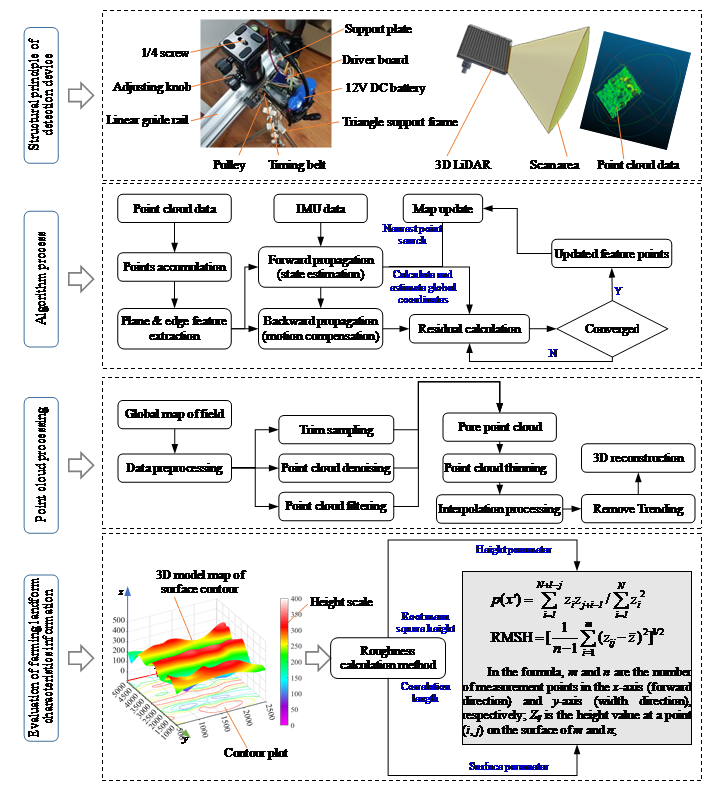
图1 地表形貌特征信息测量工作原理
土壤表面粗糙度是描述耕作地表微地貌的一项重要指标,主要体现在地表高低起伏程度,反映了土壤表面动态变化特征,可用于评价耕整机械作业质量、探究土壤-触土部件作用关系,以及为农田管理与高标准农田建设提供基础数据。
研究基于三维激光雷达与惯性测量单元信息融合方法,通过紧耦合迭代算法结合点云信息与位姿信息构建农田三维地貌图。通过统计旋耕、翻耕、垄作等三种典型农田在不同方向上的粗糙度参数,分析农田耕作地貌特征信息各向异性,探明测量过程中采样方法、数据倾斜、地表周期性结构对测量精度的影响规律。同时为了方便田间实际应用,研制了往复式地貌检测装置,实现地表形貌非接触测量,可一次性获取整个农田全景地貌。根据用户需求可调节采样样方大小和数量,减少户外工作时间、成本,有效提高了测量精度与效率。
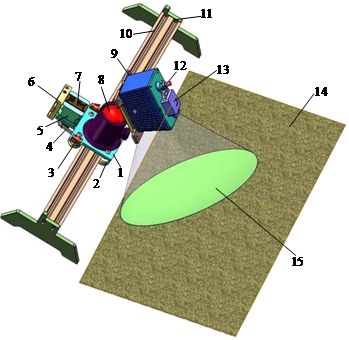
1.Support plate 2.Pulley 3.Proximity switch 4.Timing belt 5.Stepper motor 6.Motor power supply 7.Driver board 8.Pan tilt 9.Quick connect plate 10.Linear guide rail 11.Limit block 12.3D lidar 13.Inertial measurement unit 14.Farmland surface 15.Scan Area
图2 往复式地貌检测装置
我校工学院博士研究生刘国阳为论文第一作者,郑侃副教授为通讯作者。该研究得到了国家自然科学基金和学院引导专项等项目的支持。
审核人:夏俊芳
【英文摘要】
Soil surface roughness (SSR) is animportant indicator that characterizes the microtopography feature of farmlandafter tillage. It has a high practical value for sowing and seedling raising,farmland management, and drainage irrigation in agricultural production. Thetraditional method often is prone to damage the surface microstructure andresults in low efficiency and accuracy. In this study, a new method wasproposed to address the limitations of traditional measurement methods of SSR.The proposed measurement and evaluation method of farmland microtopographyfeature information based on 3D lidar and inertial measurement unit (IMU) couldbe used to quickly obtain the global point cloud map containing the height dataof the test field. Taking three different tillage methods of farmland as theresearch object, the surface root mean square height (RMSH), correlation length(CL), and their ratio were selected as roughness parameters to explore theanisotropy of microtopography features in different directions. The measurementmethod was then used to study the effects of sampling processing methods(number, interval, and length) on the measurement accuracy in both OX and OYdirections. The results indicate that under the same accuracy requirements, forthe 2 × 2 m area, the farmland with different microtopography features needs tobe processed with different sample numbers, sample intervals, and samplelengths. The optimal combination of sample parameters for Test field I issample number of 50, sample interval of 120 mm, and sample interval of 1600 mm,and that in Test field II is sample number of 50, sample interval of 160 mm,and sample interval of 1800 mm. For Test field III, the optimal combination issample number of 100, sample interval of 40 mm, and sample length of 1200 mm.The experimental results compared with the traditional method illustrate thehigh accuracy and good feasibility of the proposed method for measuring andevaluating the microtopography feature information of the farmland. The resultsof the study help to understand the microtopography features and itsparameterization of the farmland after tillage, which could further reveal therole and significance of SSR parameters in objectively evaluating farmlandtillage quality and optimizing farmland management.
